
Rare Care and Everyday Life
Monitoring and Supervision
The disease demands families and caregivers to immediately establish and closely follow a specific diet and monitor physical activity.
- Care of individuals with LC-FAOD may require an around-the-clock commitment to check for signs and symptoms of deterioration and/or fatigue.
- The management of caloric intake, avoidance of fasting (including overnight), and potential monitoring/maintenance of enteral feeding tubes may result in restrictions on time and freedom.
Health-related Quality of Life Issues
A person’s quality of life may be substantially diminished as a result of LC-FAOD.
- Physical, mental, emotional, and social functioning are negatively impacted.
- Factors that may lead to anxiety and depression include:
- Continual avoidance of triggers (exercise, exposure to viral illness, cold or hot weather)
- Risk of symptom recurrence
- Uncertainty or fear about the long-term impact of LC-FAOD
If you are experiencing any of these issues, seek the help and guidance of a trained medical professional.
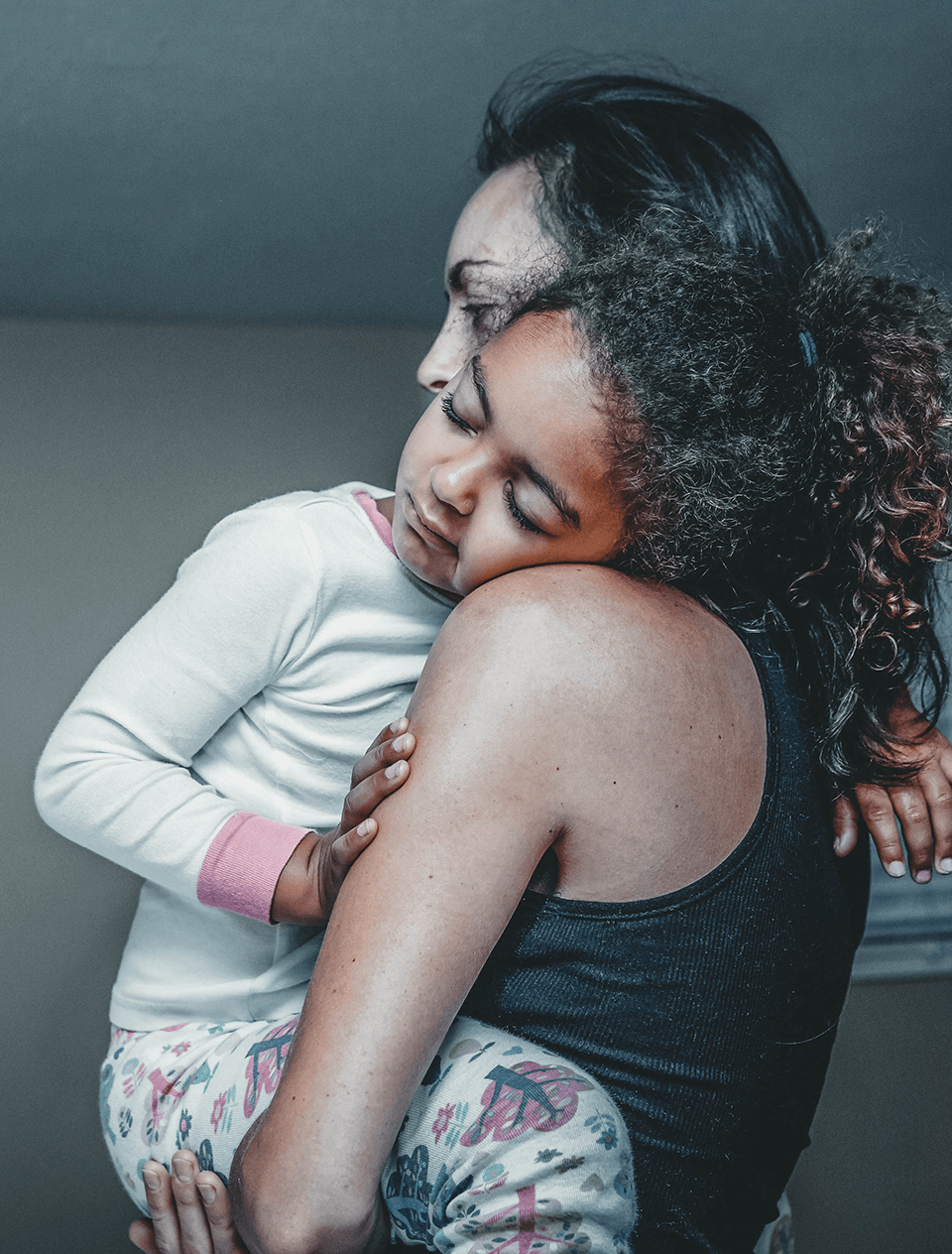
If you are experiencing any of these issues, seek the help and guidance of a trained medical professional.

How is LC-FAOD impacting you or your loved one’s life?
Take this assessment to find out and to identify topics to discuss with your healthcare team.
This LC-FAOD Self-Care Assessment will help you monitor LC-FAOD symptoms and identify topics to discuss with your LC-FAOD healthcare team.
Complete it before each visit to see how your answers may change over time.
This LC-FAOD Self-Care Assessment is provided as a tool to help you prepare for healthcare visits. Your responses are not stored or used for any purpose.
If you prefer to fill out the LC-FAOD Self-Care Assessment on paper, download it here.
Contact your healthcare team if any symptoms are concerning to you.

Activity and Symptoms
Did you know?
In LC-FAOD, when the body can’t supply enough energy to meet its needs, people may develop chronic symptoms or experience acute episodes following moderate exercise. Some people start to avoid exercise in order to avoid triggering LC-FAOD symptoms.
Activity and Symptoms - Continued
Did you know?
Chronic symptoms of LC-FAOD develop over time and may worsen over months to years. They can be brought on or made worse by fasting or illness, sustained exercise, and physiologic stress.
Acute symptoms of LC-FAOD develop suddenly. They usually appear during an illness or if you have skipped a meal, but they may also occur spontaneously or unpredictably.
Activity and Symptoms - Continued
Did you know?
LC-FAOD can cause a wide variety of symptoms that usually affect organs that use fat as a major energy source, such as the liver, heart, muscles, and eyes. People with LC-FAOD may not experience symptoms in all of these organs, and they may experience different symptoms at different times.
Activity and Symptoms - Continued
Did you know?
Keeping your healthcare team informed about new or worsening symptoms and how LC-FAOD is impacting your (or your child's) daily life can help you navigate LC-FAOD together.
Activity and Symptoms - Continued
Clinical Follow Up
Clinical Follow Up - Continued
Preparation for Discussion
Preparation for Discussion - Continued
Preparation for Discussion - Continued
Stay Informed
Sign up to receive the current disease education information in your inbox.




